Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) has revolutionized molecular biology by allowing researchers to amplify specific DNA sequences quickly, efficiently, and with remarkable precision. At the core of this transformative technology is Taq DNA Polymerase, a thermostable enzyme that drives the DNA amplification process under the rigorous conditions of thermal cycling. Understanding this enzyme including its properties, mechanism of action, applications, and best laboratory practices is essential for both novice and experienced molecular biologists seeking reliable and reproducible results.
This comprehensive guide delves into everything you need to know about Taq DNA Polymerase, from its historical discovery in thermophilic bacteria to its widespread use in modern research, diagnostics, and biotechnology applications.
What Is Taq DNA Polymerase?
Taq DNA Polymerase is a thermostable enzyme originally isolated from the thermophilic bacterium Thermus aquaticus, which was discovered in the hot springs of Yellowstone National Park during the 1960s. Its unique ability to remain stable and active at high temperatures sets it apart from DNA polymerases derived from typical mesophilic organisms, making it perfectly suited for the rigorous conditions of PCR.
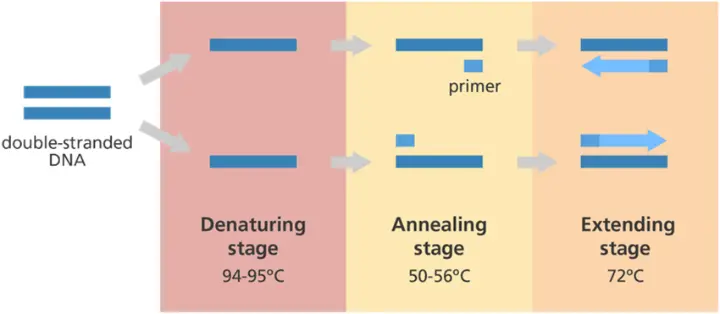
During PCR, DNA undergoes repeated cycles of:
Denaturation: the separation of the double-stranded DNA into single strands at high temperatures,
Annealing: the binding of primers to their complementary target sequences, and
Extension: the synthesis of new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the primers.
Taq DNA Polymerase withstands the high temperatures required for denaturation, enabling it to repeatedly replicate the DNA template across multiple cycles without losing activity. This thermostability, combined with its efficiency, makes Taq an essential enzyme for DNA amplification in molecular biology, diagnostics, and biotechnology research.
Key Features of Taq DNA Polymerase
Thermostability
The defining feature of Taq is its ability to withstand high temperatures without losing activity. Standard DNA polymerases denature at around 50°C, but Taq polymerase remains functional at temperatures exceeding 95°C.
High Processivity
Taq polymerase can synthesize long DNA sequences efficiently without frequently dissociating from the template, making it suitable for amplifying DNA fragments up to 4–5 kb under standard PCR conditions.
Terminal Transferase Activity
This enzyme adds a single adenine (A) nucleotide to the 3’ ends of PCR products, enabling easy cloning into T-overhang vectors, commonly used in TA cloning.
Error Rate
Taq polymerase lacks 3’→5’ exonuclease proofreading activity, which means it has a moderate error rate. This is suitable for routine PCR applications but may require high-fidelity polymerases for cloning or applications where sequence accuracy is critical.
Optimal Temperature Range
Denaturation: 94–98°C
Primer Annealing: Typically 50–65°C (depends on primer Tm)
Extension: 72°C (optimal for Taq polymerase activity)
Applications of Taq DNA Polymerase
Taq DNA Polymerase is a highly versatile enzyme that has become a cornerstone of molecular biology research due to its reliability, thermostability, and ease of use. Its applications span from routine laboratory experiments to advanced diagnostic and forensic studies. Key uses include:
- Standard PCR Amplification
Taq DNA Polymerase is widely used to amplify DNA fragments for research purposes, cloning experiments, or sequencing analyses. Its efficiency allows rapid and reproducible amplification of target sequences, even from complex genomic DNA.
2. Genotyping
Researchers use Taq polymerase for detecting genetic variations, such as single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) and small insertions or deletions. PCR-based genotyping is essential in genetic studies, personalized medicine, and plant and animal breeding programs.
3. TA Cloning
Due to its natural terminal transferase activity, Taq polymerase adds a single adenine (A) to the 3’ ends of PCR products. This feature enables seamless ligation into T-overhang vectors, simplifying the cloning process for recombinant DNA experiments.
4. Mutation Detection
Taq polymerase facilitates the identification of point mutations, small insertions, or deletions in DNA samples. Techniques like allele-specific PCR and PCR-based mutation screening rely on its efficiency and reproducibility.
5. Educational and Diagnostic Applications
Its robustness and simplicity make Taq polymerase an ideal tool for teaching laboratories, demonstrating PCR principles to students, and performing basic diagnostic assays in clinical settings.
6. Forensic and Archaeological Studies
Taq polymerase’s high-temperature stability allows amplification of DNA from trace or degraded samples, such as forensic evidence or ancient DNA, enabling researchers to analyze genetic material that would otherwise be difficult to study.
Overall, Taq DNA Polymerase’s combination of robustness, reliability, and versatility makes it indispensable for a wide range of molecular biology applications, from routine PCR to advanced genetic analysis.
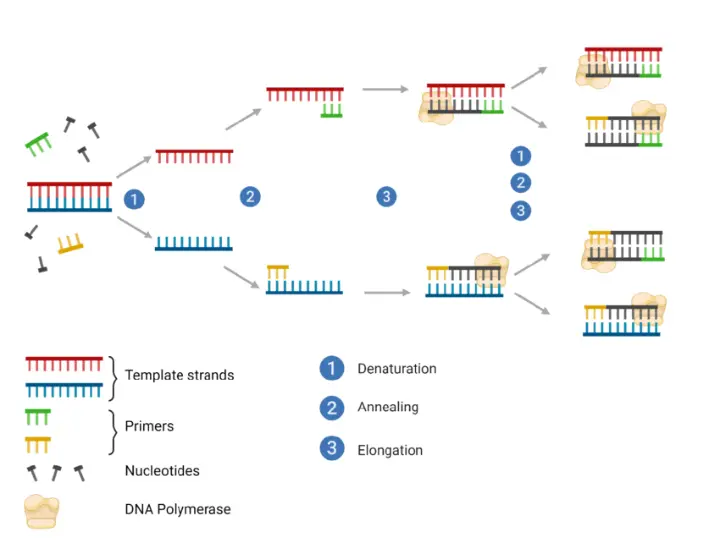
Mechanism of Action
Taq DNA Polymerase catalyzes the synthesis of DNA by adding nucleotides to the 3’ end of a primer bound to a DNA template. The process involves:
Binding: Primer anneals to the target sequence.
Extension: Taq polymerase sequentially adds nucleotides complementary to the template strand.
Thermostability: The enzyme survives repeated heating and cooling cycles, enabling multiple rounds of amplification.
Its lack of proofreading means errors can accumulate, but its speed and robustness make it ideal for routine PCR applications.
Advantages of Taq DNA Polymerase
Reliable Amplification: Consistent results across various templates.
Thermostable: Functions through repeated thermal cycles without denaturation.
Cost-Effective: Widely available and inexpensive for routine PCR.
Flexible: Compatible with most standard PCR reagents and protocols.
Conclusion
Taq DNA Polymerase remains one of the most indispensable enzymes in molecular biology. Its thermostability, robustness, and versatility make it ideal for PCR, cloning, genotyping, and many other applications. By understanding its properties and handling requirements, researchers can ensure reproducible and reliable results in all DNA amplification experiments.
For researchers seeking a reliable source of high-quality Taq DNA Polymerase, it is available here